Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, Prescription Medicine
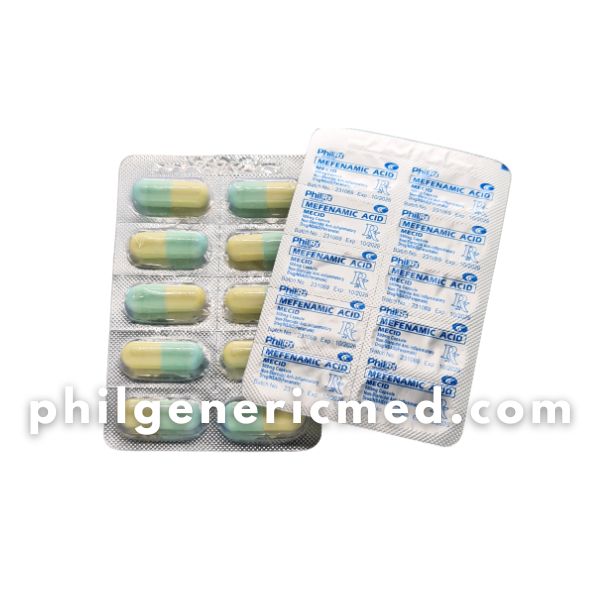
Mefenamic Acid MECID 500mg Capsule 100’s
Retail price – 150.00
Wholesale price – 100.00
Price range: ₱150.00 through ₱500.00
CompareMefenamic Acid MECID 500mg Capsule 100’s
Description:
Mefenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It works by reducing hormones that cause pain, inflammation, and fever in the body.
Uses:
-
Relief of mild to moderate pain
-
Dysmenorrhea (menstrual pain)
-
Toothache, headache, and muscle pain
-
Post-operative pain
-
Fever associated with inflammation
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 1 × 1 × 1 cm |
| Quantity | 1 Box, 3 Boxes, 5 Boxes |